Podiceps
| Podiceps Temporal range: Aquitanian to present
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Montage of eight species, featuring from left to right in three rows: P. cristatus, P. gallardoi, P. grisegena; P. auritus, P. nigricollis; P. taczanowskii, P. occipitalis, P. major. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Podicipediformes |
| Family: | Podicipedidae |
| Tribe: | Podicipedini |
| Genus: | Podiceps Latham, 1787 |
| Type species | |
| Colymbus cristatus[1] Linnaeus, 1758
| |
| Species | |
|
See text. | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Podiceps is a genus of birds in the grebe family. The genus name comes from Latin podicis, "rear-end" and ped, "foot", and is a reference to the placement of a grebe's legs towards the rear of its body.
It has representatives breeding in all continents except Antarctica. Some species are partially or entirely migratory, moving in winter to the coast or warmer climates. Most species are widespread and overall common, but three South American species each are restricted to a single country; two of them are seriously threatened and a third is already extinct.
They breed in vegetated areas of freshwater lakes, nesting on the water's edge, since their legs are set too far back for easy walking. Usually two eggs are laid, and the striped young may be carried on the adult's back. All the genus are excellent swimmers and divers, and pursue their fish prey underwater. Adults have striking breeding plumage, with no difference between the sexes. In winter, the plumage is subdued whites and greys.
Systematics
[edit]The genus Podiceps was erected by the English naturalist John Latham in 1787.[2] The type species was subsequently designated as the great crested grebe (Podiceps cristatus).[3] The genus name combines variants on the Latin podex, roughly meaning "rear-end", and pes, meaning "foot".[4]
The black-necked, Colombian, silvery, and Junin grebes are very closely related and were formerly sometimes separated as the genus Dyas. The great grebe has also sometimes been separated as the sole member of the genus Podicephorus.[5][6]
The genus contains nine species:[7]
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horned grebe or Slavonian grebe | Podiceps auritus (Linnaeus, 1758) Two subspecies
|
Eurasia and North America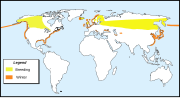
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
VU
|
| Great crested grebe | Podiceps cristatus (Linnaeus, 1758) |
Australasian, Eurasia and Africa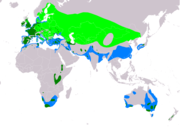
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
LC
|
| Hooded grebe | Podiceps gallardoi Rumboll, 1974 |
south-west Argentina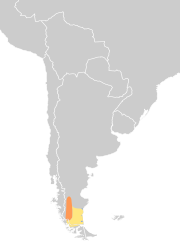
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
CR
|
| Red-necked grebe | Podiceps grisegena (Boddaert, 1783) Two subspecies
|
Eurasia and North America |
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
LC
|
| Great grebe | Podiceps major (Boddaert, 1783) Two subspecies
|
Western and southern South America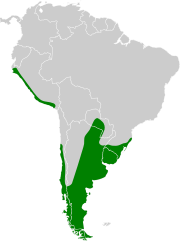
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
LC
|
| Black-necked grebe or eared grebe | Podiceps nigricollis (Brehm, 1831) Three subspecies
|
Eurasia, Africa and North America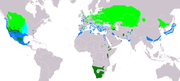
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
LC
|
| Silvery grebe | Podiceps occipitalis (Garnot, 1826) Two subspecies
|
Western and southern South America, and the Falkland Islands.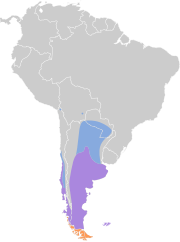
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
LC
|
| Junin grebe | Podiceps taczanowskii (Berlepsch & Stolzmann, 1894) |
west-central Peru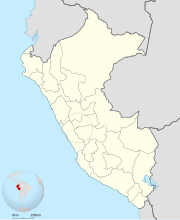
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
EN
|
| †Colombian grebe
|
Podiceps andinus (Meyer de Schauensee, 1959) |
Colombia - extinct (1977)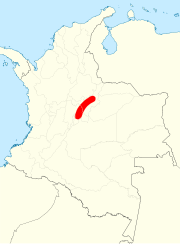
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
EX
|
Fossils
[edit]One of the very oldest fossil grebes known to date actually belongs to this genus. Regarding grebes, the fossil record leaves much to be desired, being quite complete for the last 5 million years before present but very incomplete before the Pliocene.
Fossil species of Podiceps are:
- †Podiceps arndti Chandler, 1990 (Piacenzian stage of North America)
- †Podiceps csarnotanus Kessler, 2009 (Piacenzian stage of Europe)
- †Podiceps discors Murray, 1967 (Piacenzian stage of North America)
- †Podiceps dixi Brodkorp, 1963 (Chibanian to the Tarantian stages of Florida, United States)
- †Podiceps howardae Storer, 2001 (Zanclean age of North Carolina, United States)
- †Podiceps miocenicus Kessler, 1984 (Tortonian age of Moldova)
- †Podiceps oligoceanus (Shufeldt, 1915) (Aquitanian age of North America)
- †Podiceps parvus (Shufeldt, 1913) (Gelasian to the Calabrian stages of North America)
- †Podiceps pisanus (Shufeldt, 1913) (Piacenzian stage of Italy)
- †Podiceps solidus Kuročkin, 1985 (Zanclean age of Western Mongolia)
- †Podiceps subparvus (Miller & Bowman, 1958)
- Podiceps? sp. (Late Pliocene of WC USA)
- Podiceps sp. (Early Pleistocene of Dursunlu, Turkey)[8]
Among the material assigned to P. parvus were bones of another species, which may or may not belong in this genus.[9]
References
[edit]- ^ "Podicipedidae". aviansystematics.org. The Trust for Avian Systematics. Retrieved 2023-08-05.
- ^ Latham, John (1787). Supplement to the General Synopsis of Birds. London: Printed for Leigh & Sotheby. p. 294.
- ^ Mayr, Ernst; Cottrell, G. William, eds. (1979). Check-list of Birds of the World. Vol. 1 (2nd ed.). Cambridge, Massachusetts: Museum of Comparative Zoology. p. 148.
- ^ Jobling, James A. (2010). The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London: Christopher Helm. p. 311. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4.
- ^ Ogilvie, Malcolm Alexander & Rose, Chris (2003). Grebes of the World. B. Coleman, Uxbridge. ISBN 1-872842-03-8
- ^ Harrison, Peter (1988). Seabirds (2nd ed.). Christopher Helm, London. ISBN 0-7470-1410-8
- ^ Gill, Frank; Donsker, David, eds. (2019). "Grebes, flamingos, buttonquail, plovers, painted-snipes, jacanas, plains-wanderer, seedsnipes". World Bird List Version 9.2. International Ornithologists' Union. Retrieved 16 July 2019.
- ^ Louchart, Antoine; Mourer-Chauviré, Cécile; Guleç, Erksin; Howell, Francis Clark; White, Tim D. (September 1998). "L'avifaune de Dursunlu, Turquie, Pléistocène inférieur: climat, environnement et biogéographie". Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences, Série IIA (in French and English). 327 (5): 341–346. Bibcode:1998CRASE.327..341L. doi:10.1016/S1251-8050(98)80053-0.
- ^ Murray, Bertram G. Jr (May–June 1967). "Grebes from the Late Pliocene of North America" (PDF). Condor. 69 (3): 277–288. doi:10.2307/1366317. JSTOR 1366317.










