Jordan
- For alternative meanings see: Jordan (disambiguation)
The Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, commonly called simply Jordan, is a country in the Middle East. It is bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the north-east, Saudi Arabia to the east and south, and Israel and West Bank to the west. It shares the coastlines of the Gulf of Aqaba and the Dead Sea.
| |||||
| National motto: None | |||||
 | |||||
| Official language | Arabic | ||||
| Capital | Amman | ||||
| King | Abdullah II | ||||
| Prime Minister | Faisal al-Fayez | ||||
| Area - Total |
Ranked 110th 92,300 km² |
||||
| Population - Total (2002) |
Ranked 107th 5,153,378 |
||||
| Independence - Declared |
From the League of Nations May 25, 1946 |
||||
| Currency | Jordanian dinar | ||||
| Time zone | UTC +2 | ||||
| National anthem | As-salam al-malaki al-urdoni | ||||
| Internet TLD | .JO | ||||
| Calling Code | 962 | ||||
History
Main article: History of Jordan
After World War I, various parts of the former Ottoman Empire in the Middle East were restructured. The Emirate of Transjordan was the name given to a autonomous political subdivision under British administration under the nominal auspices of the League of Nations. During this time it was ruled by King Abdullah I. For most of its history since independence from British administration in 1946, Jordan was ruled by King Hussein (1953-1999). On July 20, 1951, his grandfather King Abdullah I traveled to Jerusalem to perform his Friday prayers with his young grandson, Prince Hussein. Abdullah I was assassinated by a lone gunman on the steps of one of the holiest shrines of Islam, the Al-Aqsa Mosque. Hussein is said to have been saved from a bullet by a medal his grandfather had recently awarded him and insisted he wear. This event made him a most pragmatic ruler, and he successfully navigated competing pressures from the major powers (US, USSR, and UK), various Arab states, Israel, and a large internal Palestinian population making up a majority of Jordan's citizens, through several wars and coup attempts.
Politics
Main article: Politics of Jordan
In 1951, during the brief rule of King Talal, a new liberalized constitution was enacted. Under this Jordan is a constitutional monarchy, albeit with more power vested in the monarch than in European counterparts such as the UK or the Netherlands. Following an attempted coup d'état in 1957 king Hussein dissolved parliament. In 1989 he resumed parliamentary elections and gradually permitted political liberalization; in 1992 political parties were again allowed, and in 1993 Jordan held its first multi-party election since 1956 were held. In 1994 a formal peace treaty was signed with Israel.
Governorates
Main article: Governorates of Jordan
Jordan is divided into 12 governorates (muhafazat, singular - muhafazah):
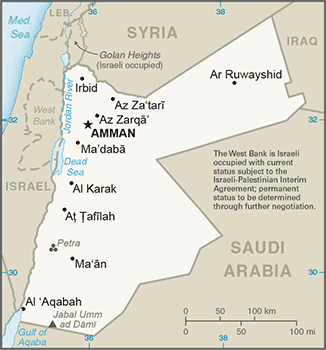
Geography
Main article: Geography of Jordan
Economy
Main article: Economy of Jordan
Jordan is a small Arab country with inadequate supplies of water and other natural resources such as oil. The Persian Gulf crisis, which began in August 1990, aggravated Jordan's already serious economic problems, forcing the government to shelve the IMF program, stop most debt payments, and suspend rescheduling negotiations. Aid from Gulf Arab states, worker remittances, and trade contracted; and refugees flooded the country, producing serious balance-of-payments problems, stunting GDP growth, and straining government resources.
The economy rebounded in 1992, largely due to the influx of capital repatriated by workers returning from the Gulf. After averaging 9% in 1992-95, GDP growth averaged only 2% during 1996-99. In an attempt to spur growth, King Abdullah has undertaken limited economic reform, including partial privatization of some state owned enterprises and Jordan's entry in January 2000 into the World Trade Organization (WTO). Debt, poverty, and unemployment are fundamental ongoing economic problems.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of Jordan
The unsuccessful 1967 Six-Day War against Israel brought massive numbers of Palestinian refugees.
Culture
Main article: Culture of Jordan
See also: Music of Jordan
Miscellaneous topics
- Communications in Jordan
- Transportation in Jordan
- Military of Jordan
- Royal Jordanian Air Force
- Foreign relations of Jordan
- Famous people from Jordan
- Royal Jordanian Airlines
- Public holidays in Jordan
External links
.com

