Kumaraswamy distribution
- For other uses, see Kumaraswamy (disambiguation).
|
Probability density function Probability density function | |||
|
Cumulative distribution function 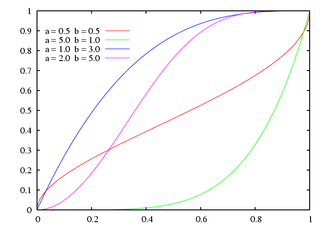 | |||
| Parameters |
(real) (real) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Support | |||
| CDF | |||
| Mean | |||
| Median | |||
| Mode | |||
| Variance | (complicated-see text) | ||
| Skewness | (complicated-see text) | ||
| Excess kurtosis | (complicated-see text) | ||
In probability and statistics, the Kumaraswamy's double bounded distribution is a family of continuous probability distributions defined on the interval [0,1] differing in the values of their two non-negative shape parameters, a and b. It is as versatile as the Beta distribution, but much simpler to use especially in simulation studies due to the simple closed form of both its pdf and cdf. The distribution form was originally presented by Poondi Kumaraswamy for variables that are lower and upper bounded.
Characterization
Probability density function
The probability density function of the Kumaraswamy distribution is
Cumulative distribution function
The cumulative distribution function is therefore
Generalizing to arbitrary range
In its simplest form, the distribution has a range of [0,1]. In a more general form, we may replace the normalized variable x with the unshifted and unscaled variable z where:
The distribution is sometimes combined with a "pike probability" or a Dirac delta function, e.g.:
Properties
The raw moments of the Kumaraswamy distribution are given by:
where B is the Beta function. The variance, skewness, and excess kurtosis can be calculated from these raw moments. For example, the variance is:
Example
A good example of the use of the Kumaraswamy distribution is the storage volume of a reservoir of capacity zmax whose upper bound is zmax and lower bound is 0 (Fletcher, 1996).
References
- Kumaraswamy, P. (1980). "A generalized probability density function for double-bounded random processes". Journal of Hydrology. 46: 79–88.
- Fletcher, S.G., and Ponnambalam, K. (1996). "Estimation of reservoir yield and storage distribution using moments analysis". Journal of Hydrology. 182: 259–275.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)


![{\displaystyle x\in [0,1]\,}](/media/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1240e42c19f013e59951788dc4e8b3205639256f)

![{\displaystyle [1-(1-x^{a})^{b}]\,}](/media/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/807738cb3750dca047e4afcd1d88665688f6de76)








