User:Volcanoguy/sandbox
Mess Creek Escarpment | |
|---|---|
 False colour image of the Kitsu Plateau; the cliff forming the western edge of the plateau is the southern portion of the Mess Creek Escarpment | |
| Coordinates: 57°34′35″N 130°47′58″W / 57.57639°N 130.79944°W[1] | |
| Location | Cassiar Land District, British Columbia, Canada[2] |
| Range | Tahltan Highland[2] |
| Part of | East-central side of Mess Creek valley and west-central side of the Mount Edziza complex[2][3] |
| Defining authority | BC Geographic Names office in Victoria, British Columbia[1][4] |
| Elevation | Above 1,700 m (5,500 ft)[2] |
| Topo map | NTS 104G10 Mount Edziza[1] |
| Designation | Mount Edziza Provincial Park[2] |
| Formations | Oldest to youngest: Raspberry Formation, Armadillo Formation, Nido Formation, Spectrum Formation, Ice Peak Formation, Big Raven Formation[5] |
| Rocks | Comendite, trachyte, hawaiite, alkali basalt[5] |
 Location in Mount Edziza Provincial Park Location in Mount Edziza Provincial Park | |
The Mess Creek Escarpment is a discontinuous cliff along Mess Creek in Cassiar Land District of northwestern British Columbia, Canada.
Name and etymology
The name of the escarpment was adopted 2 January 1980 on the National Topographic System map 104G after being submitted to the BC Geographical Names office by the Geological Survey of Canada.[2] It was required for geology reporting purposes since Jack Souther, a volcanologist of the Geological Survey of Canada, was studying the area in detail between 1970 and 1992.[6][7][8] The escarpment was named for its association with Mess Creek, a tributary of the Stikine River which flows into Sumner Strait of southeast Alaska.[1][9][10] It is one of two officially named escarpments in British Columbia, the other being the Etsho Escarpment in Peace River Land District.[11]
Geography
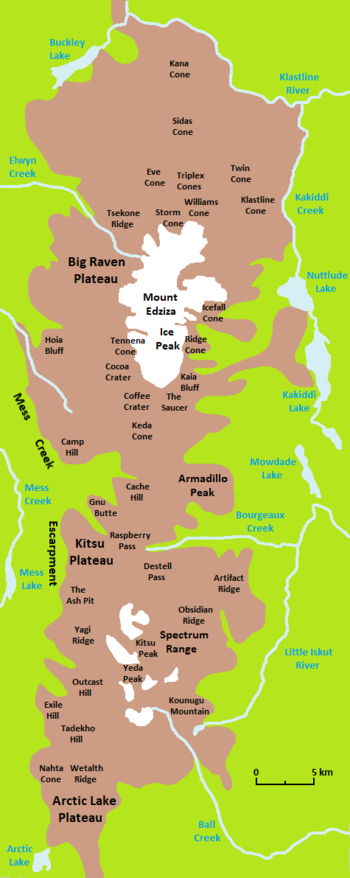
The Mess Creek Escarpment is in the Tahltan Highland east of the Boundary Ranges of the Coast Mountains and west of the Skeena Mountains and Klastline Plateau in Cassiar Land District.[2] It forms the east-central side of Mess Creek valley and the west-central side of the Mount Edziza volcanic complex, consisting of two segments separated about 5 kilometres (3.1 miles) by Raspberry and Walkout creek valleys.[2][3] The northern segment extends southeast along the southwestern side of the Big Raven Plateau for about 8 kilometres (5.0 miles) and reaches an elevation of 1,700 metres (5,500 feet). At least four unnamed streams flow down this segment of the escarpment into Mess Creek which is less than 760 metres (2,500 feet) in elevation.[2]
The southern segment reaches an elevation of more than 1,700 metres (5,500 feet) and extends generally south along the northwestern, western and southwestern edges of the Kitsu Plateau for about 10 kilometres (6.2 miles).[2][5] The Mess Creek Escarpment therefore has a total length of approximately 23 kilometres (14 miles) and rises more than 910 metres (3,000 feet) above the floor of Mess Creek valley.[2] At least five streams flow down the southern segment into Mess Creek valley, including Kitsu Creek which originates from Kitsu Peak in the Spectrum Range.[2][12] Mess Lake, an expansion of Mess Creek, lies below the southern segment of the Mess Creek Escarpment.[5][13]
Geology
Stratigraphy
The Mess Creek Escarpment is subdivided into at least six geological formations, each being the product of a distinct period of volcanic activity.[5][14] These periods of volcanic activity occurred during four magmatic cycles of the Mount Edziza volcanic complex; each cycle began with the effusion of alkali basalt and culminated with the eruption of lesser volumes of felsic magma.[15] The two oldest geological formations comprising the Mess Creek Escarpment are the Raspberry and Armadillo formations which were deposited by volcanic eruptions during the first magmatic cycle between 7.5 and 6 million years ago. Overlying these two geological formations are the Nido and Spectrum formations which were deposited between 6 and 3 million years ago during the second magmatic cycle. Volcanism during the third magmatic cycle about 1 million years ago created the Ice Peak Formation which overlies the Nido Formation. The fifth oldest geological formation comprising the Mess Creek Escarpment is the Big Raven Formation which was deposited during the fifth magmatic cycle in the last 20,000 years.[5][14]
Raspberry Formation
The Raspberry Formation consists of flat-lying basaltic lava flows interbedded with scoria and is exposed along the base of the Mess Creek Escarpment where it has an elevation of less than 1,310 metres (4,300 feet).[5] More than 180 metres (590 feet) of Raspberry lava flows are exposed in the Mess Creek Escarpment, most of which were erupted from a shield volcano that formed on a Late Miocene erosion surface.[16][17] These lava flows travelled westward into the ancestral valley of Mess Creek and originated from vents north of Raspberry Pass which were subsequently buried under younger volcanic deposits. A minimum age for the timing of Raspberry volcanism is 7.4–6.2 million years.[17]
Armadillo Formation
Basaltic lava flows of the 6.3-million-year-old Armadillo Formation are interbedded with air-fall pumice and ash flows of trachytic and rhyolitic compositions.[18] They were highly fluid and mobile at the time of their eruption as evidenced by their extreme persistence and relatively narrow thicknesses; individual basalt flows are normally less than 3 metres (9.8 feet) thick. The source of these flows was probably a cluster of vents further to the north called Sezill Volcano which may have been active prior to the onset of Armadillo volcanism.[19]
Nido Formation
Spectrum Formation
Ice Peak Formation
Big Raven Formation
Basement
Provincial park
The Mess Creek Escarpment lies at the western end of Mount Edziza Provincial Park, a protected area founded in 1972 to showcase the volcanic landscape.[2][20] This remote wilderness area of northwestern British Columbia is not accessible by motorized vehicles to help protect the very sensitive environment. Instead, access is mainly via aircraft or unmaintained hiking trails that cross creeks.[20] Mount Edziza Provincal Park covers 266,180 hectares (657,700 acres), making it one of the largest provincial parks in British Columbia.[20][21] Hunting, camping, fishing, hiking, wildlife viewing and nature studying are some of the activities available in Mount Edziza Provincial Park.[20]
Wildlife in the area includes moose, caribou, mountain goats, stone sheep, wolves, bears, squirrels, owls, ptarmigans, ravens, gyrfalcons, grouse and migratory songbirds. The climate is characterized by warm summers and cold, snowy winters; temperatures are warmest in mid-summer during the day when they may hit the 30 degrees Celsius (86 degrees Fahrenheit) range. However, temperatures can drop below freezing during summer nights, making snow or freezing rain a possibility at any time of the year.[20]
Accessibility
See also
References
- ^ a b c d "Mess Creek Escarpment". BC Geographical Names. Archived from the original on 2021-10-01. Retrieved 2024-09-22.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Telegraph Creek, Cassiar Land District, British Columbia (Topographic map) (3 ed.). 1:250,000. A502 (in English and French). Department of Energy, Mines and Resources. 1989. Archived from the original on 2021-05-02. Retrieved 2021-09-25.
- ^ a b Souther 1992, p. 32.
- ^ "Geographical Names Board of Canada". Government of Canada. Archived from the original on 2024-05-24. Retrieved 2024-08-19.
- ^ a b c d e f g Souther, J. G. (1988). "1623A" (Geologic map). Geology, Mount Edziza Volcanic Complex, British Columbia. 1:50,000. Cartography by M. Sigouin, Geological Survey of Canada. Energy, Mines and Resources Canada. doi:10.4095/133498.
- ^ "Tennena Cone". BC Geographical Names. Archived from the original on 2024-06-08. Retrieved 2024-09-25.
- ^ "Acceptance of the 1995 Career Achievement Award by Jack Souther" (PDF). Ash Fall. Geological Association of Canada. 1996. p. 3. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2018-12-05.
- ^ "Stikine volcanic belt: Mount Edziza". Catalogue of Canadian volcanoes. Natural Resources Canada. 2009-04-01. Archived from the original on 2009-06-08. Retrieved 2024-07-03.
- ^ "Mess Creek". BC Geographical Names. Archived from the original on 2024-06-07. Retrieved 2024-09-25.
- ^ National Emergency Relief: Hearings Before the Committee on Ways and Means, House of Representatives, Seventy-Second Congress, First Session on H. R. 12353. United States Government Printing Office. 1932. p. 60. OCLC 6245991. Retrieved 2024-09-25.
- ^ "Search the Canadian Geographical Names Database (CGNDB)". Government of Canada. Retrieved 2024-09-26.
- ^ "Kitsu Creek". Geographical Names Data Base. Natural Resources Canada. Retrieved 2024-09-25.
- ^ "Mess Lake". BC Geographical Names. Archived from the original on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2024-09-25.
- ^ a b Souther 1992, p. 267.
- ^ Souther 1992, pp. 1, 267, 276.
- ^ Souther 1992, pp. 6, 47.
- ^ a b Souther, J. G.; Armstrong, R. L.; Harakal, J. (1984). "Chronology of the peralkaline, late Cenozoic Mount Edziza Volcanic Complex, northern British Columbia, Canada". Geological Society of America Bulletin. 95 (3). Geological Society of America: 342–344. doi:10.1130/0016-7606(1984)95<337:COTPLC>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0016-7606.
- ^ Souther 1992, pp. 83, 267.
- ^ Souther 1992, p. 83.
- ^ a b c d e "Mount Edziza Provincial Park". BC Parks. Archived from the original on 2023-01-23. Retrieved 2024-09-26.
- ^ "Edziza: Photo Gallery". Global Volcanism Program. Smithsonian Institution. Archived from the original on 2021-09-21. Retrieved 2023-05-03.
Sources
- Souther, J. G. (1992). The Late Cenozoic Mount Edziza Volcanic Complex, British Columbia. Geological Survey of Canada (Report). Memoir 420. Canada Communication Group. doi:10.4095/133497. ISBN 0-660-14407-7.
